Share
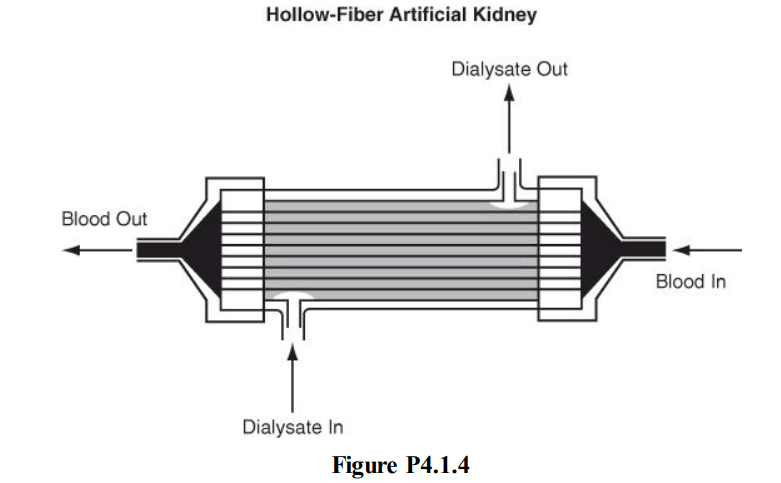
*4.1.4. Figure P4.1.4 is a sketch of an artificial kidney, a medical device used to remove waste metabolites from the blood in cases of kidney malfunction. The dialyzing fluid passes across a hollow membrane, and the waste products diffuse from the blood into the dialyzing fluid.If the blood entering the unit flows at the rate of 220 mL/min, and the blood exiting the unit flows at the rate of 215 mL/min, how much water and urea (the main waste product) pass into the dialysate if the entering concentration of urea is 2.30 mg/mL and the exit concentration of urea is 1.70 mg/mL? If the dialyzing fluid flows into the unit at the rate of 1500 mL/min, what is the concentration of the urea in the dialysate?
ReportQuestion
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
*4.1.4. Figure P4.1.4 is a sketch of an artificial kidney, a medical device used to remove waste metabolites from the blood in cases of kidney malfunction. The dialyzing fluid passes across a hollow membrane, and the waste products diffuse from the blood into the dialyzing fluid. If the blood entering the unit flows at the rate of 220 mL/min, and the blood exiting the unit flows at the rate of 215 mL/min, how much water and urea (the main waste product) pass into the dialysate if the entering concentration of urea is 2.30 mg/mL and the exit concentration of urea is 1.70 mg/mL? If the dialyzing fluid flows into the unit at the rate of 1500 mL/min, what is the concentration of the urea in the dialysate?
Leave an answer