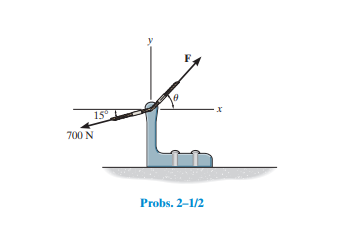
Determine the magnitude of the resultant forceFR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured clockwise fromthe positive u axis.
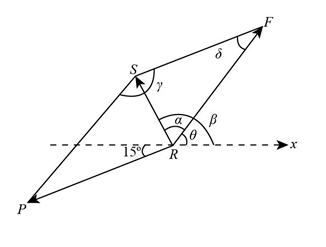
Step-by-Step Solution Step 1 We are given the value of resultant force ${{\bf{F}}_R} = {{\bf{F}}_1} + {{\bf{F}}_2}$. We are asked to estimate the magnitudes of the resultant force. Step 2 The following is the diagram from the parallelogram law of addition. The diagram of the resultant force is as follows: Step 3 The relation from […]