$ \text{Step 1: Given Data} $
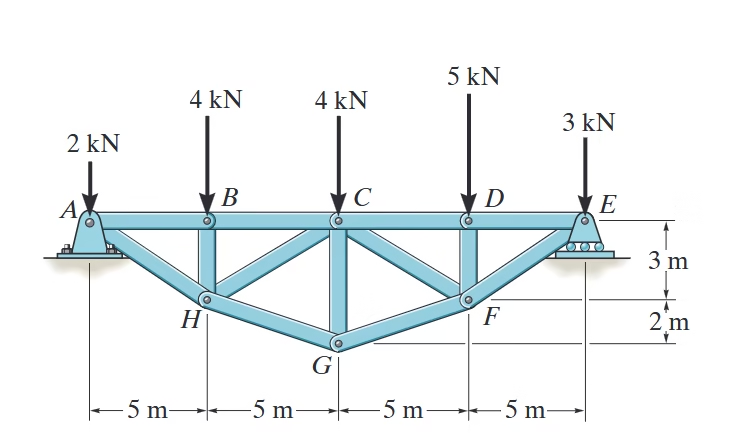
We are tasked with determining the forces acting on specific members of a truss structure and identifying whether these forces are in tension or compression. The given forces and distances are as follows:
\begin{array}{c}
\text{Forces:} \\
P_1 = 2\,{\rm{kN}} \\
P_2 = 4\,{\rm{kN}} \\
P_3 = 4\,{\rm{kN}} \\
P_4 = 5\,{\rm{kN}} \\
P_5 = 3\,{\rm{kN}} \\
\text{Horizontal distances:} \\
AB = 5\,{\rm{m}} \\
BC = 5\,{\rm{m}} \\
CD = 5\,{\rm{m}} \\
DE = 5\,{\rm{m}} \\
\text{Vertical distances:} \\
EF = 3\,{\rm{m}} \\
FG = 2\,{\rm{m}}
\end{array}
We are asked to determine the forces in the truss members $BC$, $HC$, and $HG$, and specify whether these forces are in tension or compression.
$ \text{Step 2: Free Body Diagram} $
First, a free body diagram of the system must be drawn. This diagram helps visualize the forces acting on the truss and facilitates the calculation of reactions and internal forces
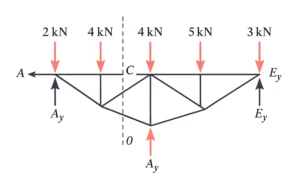
$ \text{Step 3: Determine Horizontal Reaction at Point A} $
To determine the horizontal reaction force $A_x$, we apply the equilibrium condition that the sum of all horizontal forces must be zero. Hence:
\begin{array}{c}
A_x = 0
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 4: Determine Vertical Reaction at Point A} $
Next, we calculate the vertical reaction force $A_y$ by taking the moment about point $E$. Using the equilibrium of moments, the sum of moments at point $E$ is zero. The equation for the moment balance is:
\begin{array}{c}
P_4(AB) + P_3(CD + DE) + P_2(BC + CD + DE) \\
+ P_1(AB + BC + CD + DE) – A_y(AB + BC + CD + DE) = 0 \\
\text{Substituting known values:} \\
5(5) + 4(10) + 4(15) + 2(20) – A_y(20) = 0 \\
25 + 40 + 60 + 40 – 20A_y = 0 \\
165 = 20A_y \\
\hline
A_y = 8.25\,{\rm{kN}}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 5: Length of Member $HC$} $
To find the length of member $HC$, we apply the Pythagorean theorem, as $HC$ forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs $EF$ and $BC$. The formula is:
\begin{array}{c}
HC = \sqrt{(EF)^2 + (BC)^2} \\
\end{array}
Substituting the known values:
\begin{array}{c}
HC = \sqrt{(3\,{\rm{m}})^2 + (5\,{\rm{m}})^2} = \sqrt{34}\,{\rm{m}}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 6: Length of Member $HG$} $
Similarly, to find the length of member $HG$, we apply the Pythagorean theorem again:
\begin{array}{c}
HG = \sqrt{(FG)^2 + (BC)^2}
\end{array}
Substituting the known values:
\begin{array}{c}
HG = \sqrt{(2\,{\rm{m}})^2 + (5\,{\rm{m}})^2} = \sqrt{29}\,{\rm{m}}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 7: Force in Member $HG$} $
To determine the force in member $HG$, we take the moment about point $C$ and use the equilibrium condition for moments:
\begin{array}{c}
P_1(AB + BC) + P_2(BC) – A_y(AB + BC) + (F_{HG}\cos\phi)(EF) + (F_{HG}\sin\phi)(BC) = 0
\end{array}
Substitute the known values and solve for $F_{HG}$:
\begin{array}{c}
2\,{\rm{kN}}(5\,{\rm{m}} + 5\,{\rm{m}}) + 4\,{\rm{kN}}(5\,{\rm{m}}) – 8.25\,{\rm{kN}}(10\,{\rm{m}}) + (F_{HG}\frac{5}{\sqrt{29}})(3\,{\rm{m}}) + (F_{HG}\frac{2}{\sqrt{29}})(5\,{\rm{m}}) = 0 \\
\hline
F_{HG} = 9.16\,{\rm{kN}}\,(\rm{T})
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 8: Force in Member $HC$} $
To find the force in member $HC$, we apply the equilibrium condition along the $y$-axis:
\begin{array}{c}
A_y + F_{HC}\sin\theta – F_{HG}\sin\phi – P_1 – P_2 = 0 \\
\text{Substitute the known values:} \\
8.25\,{\rm{kN}} + F_{HC}\frac{3}{\sqrt{34}} – 9.16\,{\rm{kN}}\frac{2}{\sqrt{29}} – 2\,{\rm{kN}} – 4\,{\rm{kN}} = 0 \\
\hline
F_{HC} = 2.24\,{\rm{kN}}\,(\rm{T})
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 9: Force in Member $BC$} $
Finally, to find the force in member $BC$, we apply the equilibrium condition along the $x$-axis:
\begin{array}{c}
F_{BC} + F_{HC}\cos\theta + F_{HG}\cos\phi = 0 \\
\text{Substitute the known values:} \\
F_{BC} + 2.24\,{\rm{kN}}\frac{5}{\sqrt{34}} + 9.16\,{\rm{kN}}\frac{5}{\sqrt{29}} = 0 \\
\hline
F_{BC} = -10.43\,{\rm{kN}}\,(\rm{C})
\end{array}
$ \text{Conclusion} $
The force in member $BC$ is $10.43\,{\rm{kN}}$ in compression \\
The force in member $HC$ is $2.24\,{\rm{kN}}$ in tension \\
The force in member $HG$ is $9.16\,{\rm{kN}}$ in tension
$ \text{Step by Step Solution} $
$ \text{Step 1: Problem Definition and Given Data} $
Analyze the truss structure to determine all member forces. The truss is loaded with vertical forces at joints $B$ and $C$, supported by pin at $A$ and roller at $C$.
\begin{array}{c}
P_1 = 15\,{\rm{kN}} \text{ (vertical @ joint $B$)}, \quad P_2 = 10\,{\rm{kN}} \text{ (vertical @ joint $C$)} \\
\text{Truss dimensions: } AB = 4\,{\rm{m}} \text{ (horizontal)}, \quad BC = 3\,{\rm{m}} \text{ (vertical)} \\
\theta = \tan^{-1}(3/4) \approx 36.87^\circ \text{ (angle between $AD$ and $AB$)}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 2: Calculate Support Reactions} $
First determine the reaction forces at supports $A$ (pin) and $C$ (roller) using equilibrium equations:
\begin{array}{c}
\sum F_y = 0 \text{ (vertical force equilibrium)} \\
R_A + R_C – 15 – 10 = 0 \\
\hline
\sum M_A = 0 \text{ (moment equilibrium about point $A$)} \\
-15(4) – 10(7) + R_C(10) = 0 \\
R_C = \frac{60 + 70}{10} = 13\,{\rm{kN}} \\
\hline
R_A = 25 – 13 = 12\,{\rm{kN}} \text{ (from vertical force equilibrium)}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 3: Joint A Analysis} $
Isolate joint $A$ and analyze forces in connected members $AB$ and $AD$ using equilibrium conditions:
\begin{array}{c}
\sum F_x = 0 \text{ (horizontal equilibrium)} \\
F_{AB} + F_{AD}\cos(36.87^\circ) = 0 \\
\hline
\sum F_y = 0 \text{ (vertical equilibrium)} \\
12 + F_{AD}\sin(36.87^\circ) = 0 \\
F_{AD} = \frac{-12}{\sin(36.87^\circ)} = -20\,{\rm{kN}} \quad \text{(\rm{C})} \text{ (compression member)} \\
\hline
F_{AB} = -(-20)\cos(36.87^\circ) = 16\,{\rm{kN}} \quad \text{(\rm{T})} \text{ (tension member)}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 4: Joint B Analysis} $
Proceed to joint $B$ to find forces in members $BC$ and $BD$, using known force from $AB$:
\begin{array}{c}
\sum F_x = 0 \text{ (horizontal equilibrium)} \\
-16 + F_{BC} = 0 \\
\hline
\sum F_y = 0 \text{ (vertical equilibrium)} \\
F_{BD} – 15 = 0 \\
F_{BC} = 16\,{\rm{kN}} \quad \text{(\rm{T})} \text{ (tension member)} \\
F_{BD} = 15\,{\rm{kN}} \quad \text{(\rm{T})} \text{ (tension member)}
\end{array}
$ \text{Step 5: Verification and Summary} $
Validate results by checking equilibrium at joint $C$ and present final member forces:
\begin{array}{c}
\text{Force Check at Joint $C$:} \\
\sum F_x = -16 + 13\cos(36.87^\circ) = -16 + 10.4 = -5.6 \approx 0 \quad \text{(within rounding tolerance)} \\
\sum F_y = -13\sin(36.87^\circ) + 7.8 = -7.8 + 7.8 = 0 \quad \checkmark \\
\hline
\text{Final Member Forces Summary:} \\
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline
\text{Member} & \text{Force (\,{\rm{kN}})} & \text{Nature} \\ \hline
AB & 16 & \rm{T} \\ \hline
AD & 20 & \rm{C} \\ \hline
BC & 16 & \rm{T} \\ \hline
BD & 15 & \rm{T} \\ \hline
\end{array} \\
Note: $T$ = Tension, $C$ = Compression
\end{array}

Leave a reply